Physical Therapy Strategies for Alleviating Low Back Pain
Introduction:
Living with chronic low back pain can be a significant challenge, affecting daily activities and overall well-being. However, there’s a powerful tool in the form of physical therapy that offers promise for relief. In this article, we’ll explore the realm of physical therapy and delve into how targeted exercises and lifestyle adjustments can provide respite from the discomfort of low back pain.
Understanding Low Back Pain:
Low back pain is a common ailment experienced by millions worldwide, often stemming from factors such as poor posture, muscle strain, or underlying conditions. Navigating through the pain, stiffness, and limited movement can be daunting. Yet, remember that you’re not alone – physical therapy offers a viable avenue towards finding relief.
The Role of Physical Therapy:
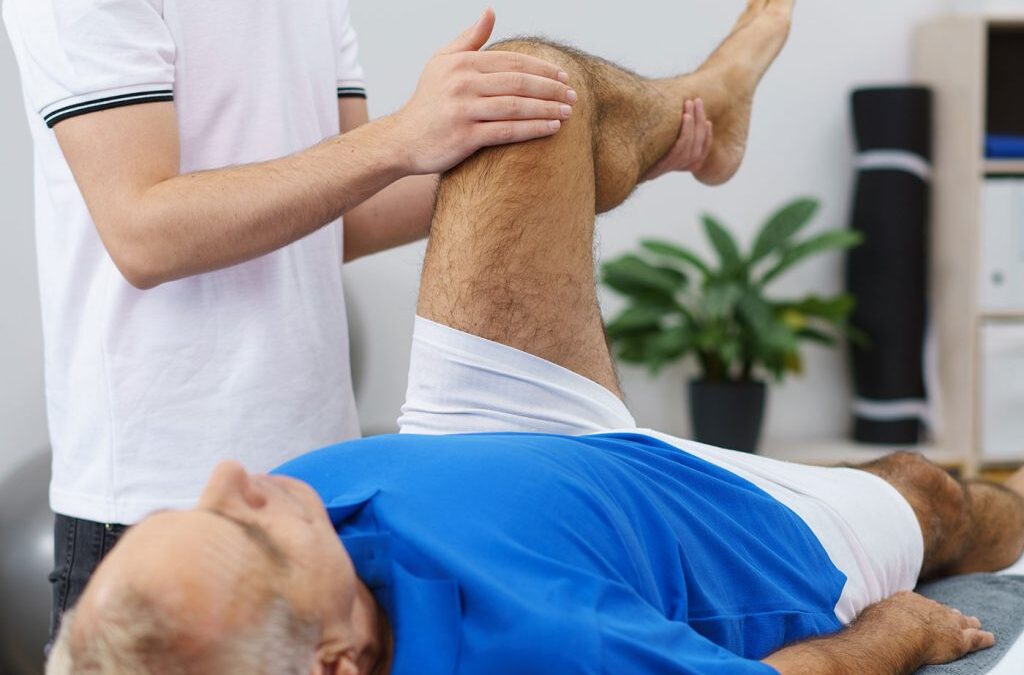
Physical therapy serves as a comprehensive approach to addressing low back pain. Through specialized exercises and techniques, physical therapists aim to alleviate pain, enhance spinal mobility, and strengthen the supporting muscles. These advantages work in concert to improve daily functionality and overall quality of life.
Effective Exercises for Low Back Pain Relief:
*Note: Before embarking on any new exercise regimen, especially if you have pre-existing medical conditions or injuries, it’s crucial to consult with your healthcare provider or physical therapist.*
Frequency: Perform the exercise routine three times per week, allowing non-consecutive days in between.
- Cat-Cow Stretch:
– Repetitions: Perform 3 sets, alternating between 10 repetitions of each movement.
– Instructions: Begin on your hands and knees in a tabletop position. Inhale as you arch your back, dropping your belly towards the floor and lifting your head and tailbone (cow pose). Exhale as you round your spine upward, tucking your chin to your chest and contracting your abdominal muscles (cat pose).
- Child’s Pose:
– Duration: Hold for 30 seconds to 1 minute.
– Instructions: Kneel on the floor, then sit back on your heels. Extend your arms forward and lower your chest towards the ground while keeping your buttocks on your heels. This stretch elongates the spine and provides relief to the lower back.
- Pelvic Tilts:
– Repetitions: Perform 2-3 sets of 15 repetitions.
– Instructions: Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Tighten your abdominal muscles to flatten your lower back against the floor, then release. This movement gently engages the core muscles and can alleviate tension in the lower back.
- Bridge Exercise:
– Repetitions: Perform 2-3 sets of 12 repetitions.
– Instructions: Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Tighten your glutes and lift your hips off the ground, creating a straight line from your shoulders to your knees. Lower your hips back down and repeat.
- Knee-to-Chest Stretch:
– Duration: Hold for 20-30 seconds on each leg.
– Instructions: Lie on your back with your knees bent. Bring one knee towards your chest and hold it with both hands. Feel a gentle stretch in the lower back. Switch legs and repeat.
Remember to execute each exercise in a controlled manner, without causing additional pain. If discomfort arises, stop immediately and consult a physical therapist or healthcare professional. As you become more accustomed to the routine, gradually increase repetitions and sets.
Lifestyle Tips to Complement Physical Therapy:
Physical therapy extends beyond exercises. To optimize your results, consider incorporating these lifestyle changes:
– Maintain good posture during daily activities to reduce strain on the lower back.
– Engage in regular aerobic exercise to promote overall fitness and circulation.
– Practice stress-reduction techniques, as stress can exacerbate low back pain.
Seeking Professional Guidance:
Prior to beginning any exercise regimen, it’s essential to consult a certified physical therapist. They will evaluate your condition and design a tailored plan to meet your specific needs and limitations. This personalized approach ensures that you achieve the best outcomes while minimizing the risk of injury.
Conclusion:
Don’t let chronic low back pain hinder your ability to enjoy life to the fullest. Embrace the potential of physical therapy to regain mobility and find relief from discomfort. Through targeted exercises and the adoption of lifestyle changes that prioritize spinal health, you’re taking proactive steps toward a future with diminished pain and enhanced well-being. Remember, seeking professional guidance is pivotal to unlocking the full benefits of physical therapy. Embark on the journey to a healthier self – your back will thank you for it.
References:
- American Physical Therapy Association. (2023). Low Back Pain. [Link](https://www.choosept.com/symptomsconditionsdetail/physical-therapy-guide-to-low-back-pain)
- Mayo Clinic. (2023). Back Pain. [Link](https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/back-pain/symptoms-causes/syc-20369906)
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. (2023). Low Back Pain Fact Sheet. [Link](https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/Patient-Caregiver-Education/Fact-Sheets/Low-Back-Pain-Fact-Sheet)
- WebMD. (2023). Back Pain Overview. [Link](https://www.webmd.com/back-pain/ss/slideshow-low-back-pain-overview)
- Cleveland Clinic. (2023). Non-Surgical Treatment for Lower Back Pain. [Link](https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/19412-non-surgical-treatment-for-lower-back-pain)